

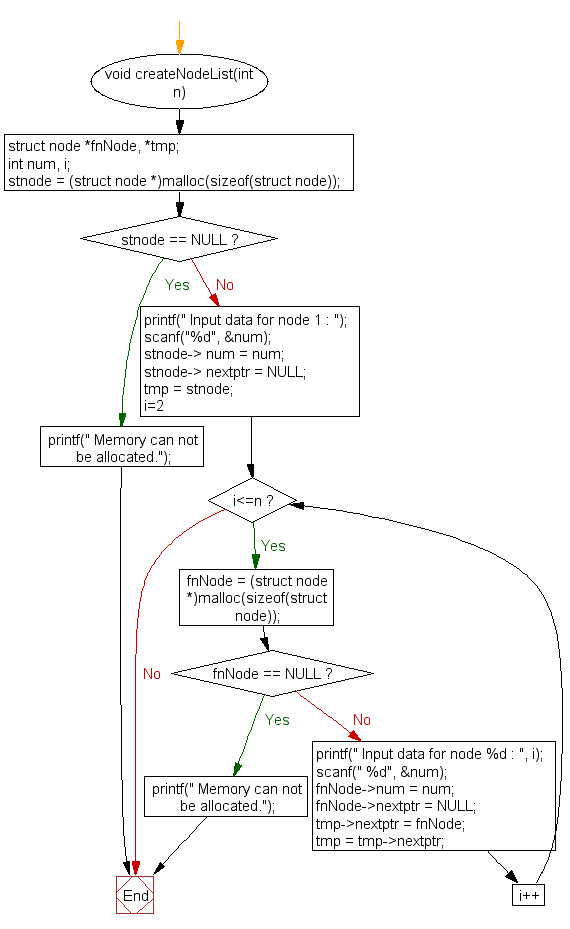
Some of the real-life applications of the linked list are as follows: Any element of a singly linked list can only be accessed in a sequential manner making binary search completely ineffective. However, with Linked List such random access is prohibited. Arrays obey this property as we can access specifically any array element in constant time. One of the important things for the binary search to work on a collection is, any location of the collection must be randomly accessible in constant time. It turns out we can’t, even if the linked list is already sorted we cannot perform the binary search over it. Can we apply the binary search on Linked List and complete our searching operation in O(log N) time? The following is the JAVA representation of a node.Īssume that the entire singly linked list is already sorted in ascending manner. The Node of the singly linked list, apart from the data, stores the address of only the next element, as shown below.

In a singly linked list, each node links to only the next node in the sequence, i.e if we start traversing from the first node of the list, we can only move in one direction(pun intended). Whereas in linked list deletion and insertion can be done in O(1).Ī Singly Linked List is a specialized case of a generic linked list. Time complexity of deletion and insertion in an array is O(N).
#SINGLY LINKED LIST FULL#
Hence linked list exploit memory to its full potential. Now we can easily store up to 4MB of linked list inside this space but 4MB of array cannot be accommodated.
#SINGLY LINKED LIST FREE#
However, the free space is in a noncontiguous manner. All the nodes of a linked list are stored at non-contiguous memory locations and are linked by pointers.įor ex: Assume the system has 4MB of free space available. While for linked list memory can be allocated dynamically. However the size of the linked list can be changed during the runtime.Īrrays requires memory allocation in a contiguous manner. Once the size of an Array is defined, it can’t be modified. Pointer to another node: It stores the link of the adjacent node.Īrray’s have a fixed size.It can be a video object, a number, a character, etc. Data: It is the actual raw information that you want to maintain.A Linked List is formed by connecting multiple nodes. This is where the Linked List comes in.Ī Linked List is a sequence of elements such that each element in the linked list points to the adjacent element in the sequence.Įach element of the Linked List is called a Node. We need something better, we need a data structure that can store a collection of objects just like an array, but whose size can be manipulated in real-time. The first thing that would have crossed your mind is maintaining an array of all images, but what if the number of images is ever increasing? Soon you’ll realize that arrays are not suited for this job, they don’t go very well with dynamic size data. How would have you maintained the huge collection of images? Have you ever wandered through Instagram feeds? Yeah, one image after another it keeps on scrolling, it’s infinite, it’s almost never-ending!īut have you ever wondered how it all works? Imagine, if you were the engineer who was asked to develop this feature, how would you have approached this problem? Takeaways Complexity of singly linked list A singly linked list is a type of linked list that is unidirectional, that is, it can be traversed in only one direction from head to the last node (tail).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
